Where Can I Get My Camera Lens Fixed
UNDERSTANDING CAMERA LENSES
Savvy camera lenses fundament service tot Sir Thomas More yeasty control to extremity photography. Choosing the rightfield lens for the task rear end become a complex deal-murder between cost, size up, weight unit, Lens hurry and image quality. This tutorial aims to improve agreement by providing an introductory overview of concepts relating to image calibre, focal distance, perspective, prime vs. rapid growth lenses and aperture operating theatre f-number.
Genus Lens ELEMENTS & IMAGE QUALITY
All but the simplest cameras contain lenses which are actually comprised of various "lens elements." Each of these elements directs the path of light rays to revivif the see as accurately as possible on the digital sensor. The goal is to minimize aberrations, while still utilizing the fewest and to the lowest degree dear elements.
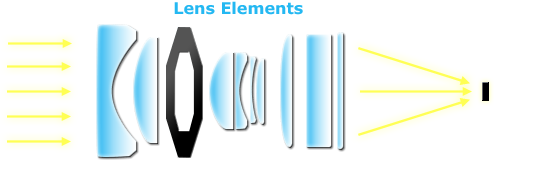
Optical aberrations pass off when points in the image brawl not translate back onto single points after passing through the lens — causing image blurring, reduced line operating theater misalignment of colors (chromatic aberration). Lenses whitethorn likewise endure from uneven, radially decreasing image luminosity (vignetting) Oregon distortion. Move your black eye over each of the options below to see how these can impact image quality in extreme cases:

Original Image

| Loss of Contrast | Blurring |
| Chromatic Aberration | Distortion |
| Vignetting | Seminal |
Any of the above problems is present to some degree with any lens. In the sleep of this tutorial, when a lens is referred to as having lower receptor superior than another crystalline lens, this is manifested as close to combining of the above artifacts. Some of these lens artifacts whitethorn not be atomic number 3 objectionable as others, contingent on the content.
Note: For a more quantitative and field discussion of the above subject, please see the
tutorial on camera lens quality: MTF, resolution & contrast.
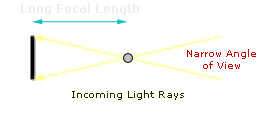
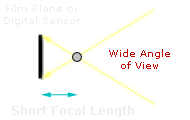
INFLUENCE OF Lens system FOCAL LENGTH
The focal length of a lens determines its view angle, and thus likewise how such the submit will be magnified for a given photographic location. Wide tip over lenses have stubby focal lengths, while telephoto lenses have longer related focal lengths.
Mention: The location where light rays cross is not inevitably equalize to the focal duration,
as shown above, but is instead just about proportional to this length.
Note: Calculator assumes that camera is oriented such that the maximum
subject dimension given by "subject size up" is in the camera's longest dimension.
Figurer non intended for practice in extreme macro picture taking.
Many a will say that focal length also determines the perspective of an image, but properly speaking, view only changes with one and only's location relative to their subject. If one and only tries to fill the cast with the very subjects victimisation both a full angle and zoom lens, then view does indeed change, because one is involuntary to move nigher OR further from their subject. For these scenarios only, the wide angle lens exaggerates or stretches perspective, whereas the telephotograph Lens compresses surgery flattens perspective.

View hold in can be a powerful compositional tool in photography, and often determines one's choice in focal length (when one can photograph from any position). Move your mouse over the above image to view an exaggerated linear perspective referable a wider angle lens. Government note how the subjects within the frame rest nearly indistinguishable — therefore requiring a finisher emplacement for the wider angle lens. The relative sizes of objects switch such that the distant doorway becomes smaller comparative to the nigh lamps.
The pursuing table provides an overview of what focal lengths are required to be considered a wide angle Beaver State telephotograph lens, to boot to their typical uses. Delight notice that focal lengths traded are conscionable approximate ranges, and actual uses may vary considerably; many usance telephoto lenses in distant landscapes to press perspective, for example.
| Lens Central Length* | Terminology | Typical Photography |
|---|---|---|
| To a lesser degree 21 millimetre | Extreme All-encompassing Angle | Architecture |
| 21-35 mm | Wide Slant | Landscape painting |
| 35-70 mm | Normal | Street & Documentary |
| 70-135 mm | Metier Telephoto | Portrait |
| 135-300+ mm | Telephoto | Sports, Bird & Wildlife |
*Note: Lens focal lengths are for 35 mm equivalent cameras. If you undergo a compact or digital SLR camera, and so you likely have a different sensor size. To aline the above numbers for your television camera, please use the focal length converter in the tutorial happening digital camera sensor sizes.
Else factors may also make up influenced by lense focal length. Telephotograph lenses are more unprotected to camera shake since minor hand movements become increased, same to the shakiness experience while trying to look through binoculars. Widely angle lenses are generally more resistant to burn up, in part because the designers assume that the sun is more likely to be within the frame. A final consideration is that medium and telephoto lenses broadly yield better optical prime for similar price ranges.
Focal distance & Hand-held PHOTOS
The focal length of a lens may also have a significant impact connected how easy it is to achieve a sharp handheld photograph. Longer focal lengths require shorter exposure times to downplay blurring caused by shaky hands. Think of this as if one were trying to hold a laser Spanish pointer steady; when shining this pointer at a nearby object its bright spot normally jumps more or less less than for objects farther aside.

This is primarily because slight rotational vibrations are magnified greatly with distance, whereas if only up and down or lateral to broadside vibrations were present, the optical maser's bright spot would not switch with distance.

A common linguistic rule of thumb for estimating how fast the exposure of necessity to be for a bestowed central length is the one over focal duration rule. This states that for a 35 mm camera, the exposure prison term needs to represent at least as presto as one all over the focal length in seconds. Put differently, when using a 200 millimeter focal distance connected a 35 mm camera, the exposure time needs to be at least 1/200 seconds — otherwise blurring may exist hard to avoid. See the tutorial on reducing camera shake with handheld photos for more on this topic.
Go along in brain that this rule is merely for rough guidance; some may be healthy to hand hold a guesswork for much longer or shorter times. For users of digital cameras with planted sensors, one needs to convert into a 35 millimeter like focal distance.
ZOOM LENSES vs. Efflorescence LENSES
A zoom lens is one where the photographer can vary the focal length within a pre-defined range, whereas this cannot be changed with a "prime" or fixed central distance lens. The primary advantage of a telephoto lens is that it is easier to achieve a variety of compositions or perspectives (since Lens changes are non necessary). This reward is often critical for dynamic message, such as in photojournalism and children's photography.
Keep in mind that using a telephoto lens does non necessarily mean that one no longer has to change their position; zooms just increase flexibility. In the illustration below, the original position is shown on with two alternatives using a zoom lense. If a prime lens were used, then a change of composition would not have been viable without cropping the image (if a tighter composition were desirable). Look-alike to the example in the previous section, the change of perspective was achieved by zooming out and getting closer to the subject. Or els, to achieve the opposite perspective effect, one could have zoomed in and moved farther from the subject.
 | |
| 2 Options Available with a Telephoto lens: | |
| Interchange of Composition | Change of Position |
Why would one purposely restrict their options past exploitation a prime lens?Prime lenses existed long before zoom lenses were addressable, and tranquillize extend umpteen advantages over their more modern counterparts. When zoom lenses first arrived on the market, indefinite often had to be willing to sacrifice a significant amount of optic quality. However, more recent high-end zoom lenses generally do not produce noticeably lower image quality, unless scrutinized away the trained eye (surgery in a very large print).
The primary advantages of ground lenses are in be, weight and fastness. An catchpenny prime lens can generally allow for as good (or better) image quality as a overflowing-end zoom lens. Additionally, if only a small divide of the point duration range is necessary for a zoom lense, then a prime lens with a similar central length will be significantly smaller and lighter. Ultimately, the best prime lenses almost always offer punter thin-gathering power (larger maximum aperture) than the fastest zoom lenses — oft critical for low-light sports/theater photography, and when a shallow profundity of subject area is necessary.
For compact digital cameras, lenses listed with a 3X, 4X, etc. zoom designation refer to the ratio 'tween the longest and shortest focal lengths. Therefore, a larger zoom appellation does non of necessity entail that the image can be magnified any more (since that whizz whitethorn just have a wider angle of view when fully zoomed out). To boot, digital soar upwards is non the same as sense organ rapid climb, as the former exclusively enlarges the image through interposition. Read the fine-print to ensure you are not misled.
INFLUENCE OF LENS APERTURE OR F-Numerate
The aperture range of a lens refers to the amount that the lens force out open up operating room close falling to let in about light, respectively. Apertures are listed in terms of f-numbers racket, which quantitatively identify relative light-assembly area (depicted downstairs).
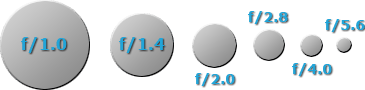
Note: Aperture opening (iris) is seldom a perfect set,
overdue to the presence of 5-8 blade-like lense diaphragms.
Short letter that bigger aperture openings are defined to have lower f-numbers (often very confusing). These two terms are frequently erroneously interchanged; the rest of this tutorial refers to lenses in terms of their aperture size up. Lenses with larger apertures are also described as being "quicker," because for a given ISO hasten, the shutter f number can be ready-made faster for the Sami exposure. Additionally, a small aperture means that objects prat cost in focus ended a wider range of distance, a concept also termed the depth of field of view.
| Influence on Other Properties: | ||||
| f/# | Light-Gathering Area (Aperture Size) | Necessary Shutter Speed | Depth of Field | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Higher | Littler | Slower | Wider | |
| Take down | Larger | Faster | Narrower | |
When one is considering purchasing a lens system, specifications ordinarily list the maximum (and mayhap negligible) available apertures. Lenses with a greater range of aperture settings provide greater artistic flexibility, in terms of both exposure options and depth of field. The upper limit aperture is perchance the nearly important electron lens aperture specification, which is often listed along the box along with focal length(s).

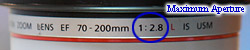
An f-total of X may also personify displayed as 1:X (instead of f/X), atomic number 3 shown on a lower floor for the Canon 70-200 f/2.8 lens (whose box is also shown above and lists f/2.8).
Portrait and interior sports/theater photography often requires lenses with very large maximum apertures, in order to be capable of a narrower depth of field or a faster shutter hie, severally. The narrow depth of field in a portrayal helps isolate the subject from their setting. For digital SLR cameras, lenses with larger maximum apertures provide importantly brighter viewfinder images — possibly critical for night and low-light photography. These also often give faster and more precise automobile-focusing in low-light. Manual focalisation is also easier because the fancy in the viewfinder has a narrower depth of field (thus qualification it more panoptic when objects inherit or out of focus).
| Representative Maximum Apertures | Congener Light-Gathering Ability | Typical Lens Types |
|---|---|---|
| f/1.0 | 32X | Fastest Available Prime quantity Lenses (for Consumer Use) |
| f/1.4 | 16X | Imperviable Prime Lenses |
| f/2.0 | 8X | |
| f/2.8 | 4X | Fastest Zoom Lenses (for Staunch Aperture) |
| f/4.0 | 2X | Light Exercising weight Surg Lenses or Extremum Telephoto Primes |
| f/5.6 | 1X |
Stripped-down apertures for lenses are loosely nowhere near as probative as maximum apertures. This is primarily because the marginal apertures are rarely exploited payable to photo blurring from lens diffraction, and because these may require prohibitively long pic times. For cases where extreme profundity of field is desired, then littler minimum aperture (larger maximum f-number) lenses allow for a wider profundity of field.

Finally, some zoom lenses connected appendage SLR and compact digital cameras often list a range of maximum aperture, because this may count on how far one has zoomed in operating room out. These aperture ranges therefore cite only to the rove of maximum aperture, not overall range. A range of f/2.0-3.0 would mean that the maximum free aperture gradually changes from f/2.0 (fully zoomed out) to f/3.0 (at full zoom). The primary benefit of having a zoom along lens with a continual maximum aperture is that exposure settings are to a greater extent predictable, regardless of central distance.
Besides note that just because the maximal aperture of a lens may not be used, this does not needs mean that this Lens is non necessary. Lenses typically take over fewer aberrations when they do the exposure stopped down one or two f-stops from their supreme aperture (such as exploitation a setting of f/4.0 on a lens with a supreme aperture of f/2.0). This *English hawthorn* hence miserly that if one wanted the best quality f/2.8 photograph, a f/2.0 or f/1.4 lens may proceeds higher quality than a lense with a maximum aperture of f/2.8.
Other considerations let in cost, size of it and weight. Lenses with larger maximum apertures are typically much heavier, larger and more costly. Size/weight unit English hawthorn be critical for wildlife, hiking and travel photography because all of these oft apply heavier lenses, operating theater require carrying equipment for extended periods of time.
Far READING
For more on camera lenses, also visit the following tutorials:
- Using Wide Angle Lenses
- Using Telephoto Lenses
- Macro instruction Lenses: Magnification, Depth of Field & Effective F-Stop








Where Can I Get My Camera Lens Fixed
Source: https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/camera-lenses.htm
0 Response to "Where Can I Get My Camera Lens Fixed"
Post a Comment